readfile
(PHP 4, PHP 5)
readfile — Outputs a file
Description
$filename
[, bool $use_include_path = false
[, resource $context
]] )Reads a file and writes it to the output buffer.
Parameters
-
filename -
The filename being read.
-
use_include_path -
You can use the optional second parameter and set it to
TRUE, if you want to search for the file in the include_path, too. -
context -
A context stream resource.
Return Values
Returns the number of bytes read from the file. If an error
occurs, FALSE is returned and unless the function was called as
@readfile(), an error message is printed.
Examples
Example #1 Forcing a download using readfile()
<?php
$file = 'monkey.gif';
if (file_exists($file)) {
header('Content-Description: File Transfer');
header('Content-Type: application/octet-stream');
header('Content-Disposition: attachment; filename='.basename($file));
header('Expires: 0');
header('Cache-Control: must-revalidate');
header('Pragma: public');
header('Content-Length: ' . filesize($file));
readfile($file);
exit;
}
?>
The above example will output something similar to:
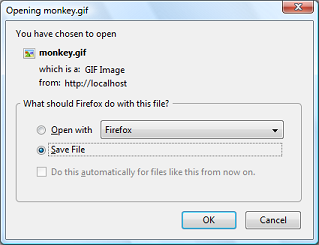
Notes
Note:
readfile() will not present any memory issues, even when sending large files, on its own. If you encounter an out of memory error ensure that output buffering is off with ob_get_level().
A URL can be used as a filename with this function if the fopen wrappers have been enabled. See fopen() for more details on how to specify the filename. See the Supported Protocols and Wrappers for links to information about what abilities the various wrappers have, notes on their usage, and information on any predefined variables they may provide.
Note: Context support was added with PHP 5.0.0. For a description of contexts, refer to Streams.
See Also
- fpassthru() - Output all remaining data on a file pointer
- file() - Reads entire file into an array
- fopen() - Opens file or URL
- include - include
- require - require
- virtual() - Perform an Apache sub-request
- file_get_contents() - Reads entire file into a string
- Supported Protocols and Wrappers